Arthrosis is a joint pathology accompanied by damage to cartilage tissue. Synonyms of arthrosis are gonarthrosis, deforming osteoarthrosis, osteoarthritis - all these terms mean the development of degenerative processes in the cartilage covering the epiphyses of the joint bones.
Despite the fact that the lesion affects only the cartilaginous structures, all joint elements are affected - the capsule, the synovial membrane, the subchondral bones, as well as the ligaments and muscles surrounding the joint. Arthrosis can affect one or more joints.
The most common localized forms of the disease have their own names: arthrosis of the hip joint is called coxarthrosis, arthrosis of the knee joint is called gonarthrosis.
Classification and causes
Knee arthrosis can be primary or secondary. The first group includes those pathologies whose cause has not been established, that is, they are of idiopathic origin. Secondary arthrosis occurs after injury, against the background of congenital disorders and systemic diseases.
The causes of arthrosis of the knee joint are as follows:
- autoimmune pathologies - rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, etc. ;
- arthritis caused by a specific infection (syphilis, gonorrhea, encephalitis);
- hereditary diseases of the locomotor system and joints, type 2 collagen mutations.
There are also several factors that negatively affect the joints and can cause pathological changes in them:
- old age, overweight, osteoporosis;
- hormonal changes, including a decrease in estrogen synthesis in postmenopausal women;
- metabolic disease;
- lack of microelements and vitamins in the diet;
- congenital and acquired deformities of skeletal bones;
- hypothermia and poisoning with toxic substances;
- permanent injury to the joint during sports training or hard work;
- operations on the knee joint - for example, removal of the meniscus.
Symptoms and stages
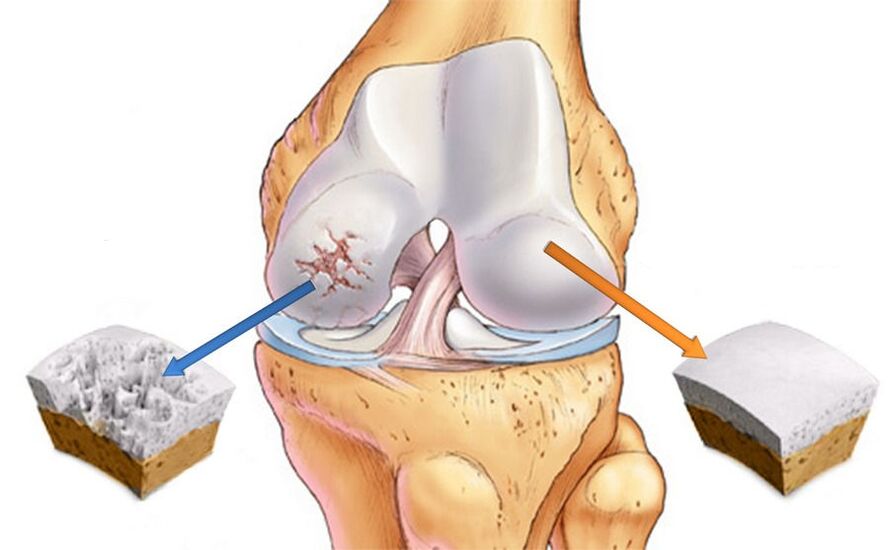
Deforming arthrosis of the knee joint is characterized by intracellular changes at the morphological, molecular, biochemical and biomechanical levels. The consequence of the pathological process is the softening, fibrosis and reduction of the thickness of the articular cartilage. In addition, the surfaces of the articular bones become denser, and bone spines - osteophytes - appear on them.
DOA of the knee joints develops in 3 stages, and in the early stage it may only show mild pain and discomfort after prolonged physical activity. Sometimes one of the characteristic symptoms of arthrosis appears - morning stiffness. Then changes occur in the synovial membrane and the composition of the intra-articular fluid.
Because of this, the cartilage tissue does not receive enough nutrients, and its ability to withstand pressure begins to decrease. Therefore, pain occurs with intense training and long walks.
In the second stage of arthrosis, the destruction of the cartilage tissue progresses, and part of the increased load is taken up by the joint surfaces of the bones. Because there is not enough area for support, the edges of the bones become enlarged due to osteophytes. The pain does not go away at rest, as before, and even bothers me at night.
The time of morning stiffness also increases, and it takes a long time to "work out" the leg to be able to walk normally. In addition, when the limb is bent, cracking and clicking sounds are heard, accompanied by a sharp pain. It is not always possible to fully bend the leg, it seemsthat it is stuck and further attempts result in a harsh crunch and pain.
Due to pain during any movement, a person tends to move less, which negatively affects the muscles surrounding the joint. The change in the size of the epiphyses of the bones leads to displacement of the axis of the limb and the development of deformity. The joint capsule becomes stiffer as the amount of fluid inside decreases. When osteophytes compress the surrounding soft tissues, synovitis and chronic inflammation occur.
When moving to the 3rd stage, the signs of arthrosis of the knee joint become very serious - the pain does not go away even at night, the motor skills practically stop, the leg seems crooked and does not bend. The third degree of arthrosis is characterized by an X- or O-shaped deformity, which makes movement extremely difficult. The advanced form of deforming gonarthrosis can only be treated surgically.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing arthrosis of the knee joint is not particularly difficult, the doctor can assume gonarthrosis based on existing symptoms and characteristic visual signs. X-rays are taken to confirm the diagnosis. The images show narrowing of the interarticular space, bone growths and subchondral osteosclerosis of the bones.
X-rays are used to determine the cause of the disease. Bone deformations are particularly visible in post-traumatic arthrosis. If cartilage degeneration is caused by arthritis, defects can be seen along the edges of the bones, as well as periarticular osteoporosis and atrophy of bone structures. In various congenital disorders, distortion of the axis of one of the bones is observed, which led to the incorrect distribution of the load and the occurrence of secondary osteoporosis.
Treatment
The treatment of gonarthrosis of the knee joint has 3 main goals - restoring the cartilage tissue, improving the mobility of the joint and slowing down the progression of the disease. They attach great importance to eliminating or weakening symptoms - reducing the intensity of pain and inflammation. Medicines, physiotherapy and exercise therapy are used to solve these problems. In order to achieve the maximum effect of the therapy, dosed physical activity and adherence to the orthopedic regimen are necessary.
Medical treatment of knee arthrosis includes the use of pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as chondroprotectors that promote the regeneration of cartilage tissue. Medicines can be prescribed in the form of injections, tablets, ointments and gels.
If primary arthrosis of the knee joint is diagnosed, physiotherapy methods, physical therapy and massage are used during the treatment. The early stages of the disease are much easier to treat and you can expect a full recovery. Losing weight is an important condition in order to reduce the load on the painful joint.
Treatment of arthrosis of the second stage of the knee joint necessarily includes exercise therapy, wearing orthopedic devices and following a diet. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors, and intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections are prescribed to relieve pain.
Acute arthrosis is characterized by severe pain, for which traditional NSAIDs are not sufficient. In this case, strong painkillers and glucocorticosteroid injection into the joint cavity are used.
If conservative methods are ineffective, surgery is performed, which can be corrective or radical (replacement of the joint with a prosthesis).
The deforming arthrosis of the knee joint of the third stage is characterized by the complete absence of the interarticular space, which is replaced by bone structure. This condition requires surgical intervention, as other methods are powerless in this case.
NSAIDs and corticosteroids
In order to save patients from physical and mental suffering, the therapy of acute arthrosis begins with pain relief. Medicines belonging to the NSAID group, available in tablets or topically, have been shown to be effective.
The pain-relieving effect does not always appear immediately, but after two or three days it reaches its peak and the pain goes away. The duration of NSAID treatment is limited to two weeks, as longer use increases the risk of side effects. People with gastrointestinal problems and high blood pressure should be especially careful.
If there is no result, hormonal drugs are prescribed to relieve inflammation. In the case of left-sided gonarthrosis, drugs are injected into the left knee, and in the case of right-sided - into the right side.
Hormonal injections can be given once every 10 days, not more often. The indication for such treatment is the accumulation of a large amount of fluid in the joint due to inflammation. As the symptoms subside, they switch to pill form.
Chondroprotectors and hyaluronic acid
Chondroprotective agents act in three directions - they restore damaged cartilage tissue, reduce pain and eliminate inflammatory reactions. Taking chondroprotectors helps to normalize the composition and properties of synovial fluid, nourishes cartilage and protects pain receptors from irritation.
As a result, the destruction of cartilage structures and, consequently, the progression of the disease slows down. After taking the medicine, the shock-absorbing and lubricating function of the joint is restored.
In the early stages of the disease, chondroprotectors can be used in the form of ointment or gel. However, intra-articular injections are the most effective. Modern methods of treating arthrosis include the use of combined agents, which contain not only chondroprotective substances, but also anti-inflammatory components and vitamins.
Hyaluronic acid is the main component of synovial fluid, responsible for its viscosity and texture. It is actually a biological lubricant that provides flexibility, elasticity and strength to the cartilage.
With the development of joint pathologies, the amount of hyaluronic acid can decrease by 2-4 times, which inevitably leads to excessive friction of the bones. With the intra-articular injection of hyaluronic, the function of the knee is normalized and the person can move normally.
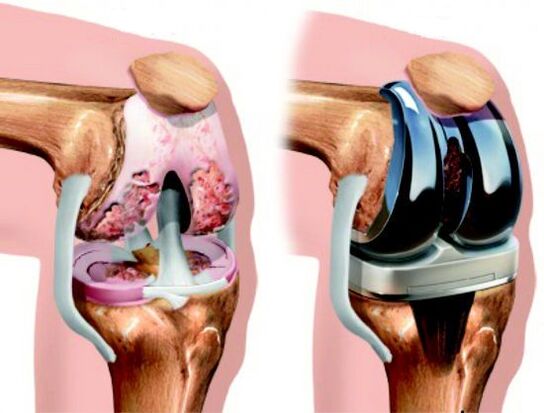
Surgery
Surgery is a radical method by which the functionality of the joint is partially or completely restored. The degree of intervention can be different and depends on the stage of arthrosis. The most gentle operation is arthroscopy - the rehabilitation period after the operation is the least painful for the patient.
Important:arthroscopy can be performed not only for treatment, but also for diagnosing joint pathology. This procedure allows you to identify damage that is not accessible to other tests.
Arthroscopy aims to prolong the life of the joint by removing dead and damaged tissue from the joint cavity. As a result, pain disappears, resistance to stress increases, and motor activity returns.
In case of significant deformities, osteotomy is recommended - creating an artificial bone fracture in a specific area. Knee osteotomy literally means "cutting the bones" - during the operation, the surgeon removes the wedge-shaped segment of the femur or tibia, and then unites the bones in the most physiological position. If necessary, the resulting gap is filled with bone graft. During the healing period, the structurefixed with special clamps.
Endoprosthesis replacement is an alternative to the outdated arthrodesis procedure, the essence of which is partial or complete replacement of the diseased joint with a prosthesis. As a result, knee function is completely restored in more than 90% of cases, significantly improving the quality of life of patients.

Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures play an important role in the treatment of arthrosis, due to their beneficial effect on damaged joints. Physiotherapy accelerates regeneration processes, eliminates pain and muscle spasms. In addition, some procedures allow the administration of drugs through the skin, thereby reducing the dose of oral drugs.
The following techniques are recommended for injured joints:
- magnet therapy;
- mid-wave ultraviolet (WUV);
- infrared laser;
- UHF;
- ultrasound;
- diadem and sinusoidal modulated currents (amplipulse therapy);
- With Darson.
Effective procedures for arthrosis are also therapeutic baths - radon, hydrogen sulfide, bischofite, mineral matter and sage. They have anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving and joint-restoring effects.
Finally
If you suspect arthrosis of the knee, consult an orthopedic doctor or a traumatologist who diagnoses and treats these pathologies. In order not to aggravate the disease, it is necessary to avoid excessive physical activity on the legs and get rid of excess weight.
There is no special diet for arthrosis, but it is recommended to avoid concentrated meat and fish soups, fatty meats and smoked meats, as well as to reduce the consumption of table salt. The diet should be dominated by foods rich in vitamins and minerals, as well as vegetable oils. In addition, it is advisable to organize a fasting day once a week - kefir, cottage cheese or fruit and vegetables.
In order to strengthen the muscular ligaments of the lower limbs and increase blood flow, therapeutic exercises should be performed regularly, which are individually selected by a physical therapy instructor.
Thus, taking medicines, physical procedures, a balanced diet and exercise are what definitely help patients with arthrosis. And to avoid a traumatic operation, you need to seek medical help as soon as possible. To be healthy!